Course: Security Management (IV2022) Year: 2011 Spring
Investigation of Cyber-attacks among Asian Countries
(China, Japan, Philippine and Vietnam)
Yuanjun Song, Jing Ba and Huan Meng
Abstract
With the fast development of internet and information technology cyber attacks such as website defacement has appeared all over the world. The internet resource about business, technology and even government has been targeted by hackers. And the purpose of cyber attack like defacement is changing from personal purpose to business competition and even political conflict. In this report we have described the situation of cyber attacks, in particular defacement, between Asian countries such as China, Japan, Vietnam and Philippine. And related articles, news and research statistics have been reviewed in the report.
Definition
Website defacement is a kind of attack which modifies the visual appearance of the website or a webpage in it. Attackers break into web servers and replace the hosted websites with their own. One of the most used methods to deface is the SQL Injection which can be utilized by attackers to obtain administrative access in order to change pages or more dangerous actions.
[Wikipedia 2012]
“A denial-of-service attack (DoS attack) or distributed denial-of-service attack (DDoS attack) is an attempt to make a machine or network resource unavailable to its intended users. Although the means to carry out, motives for, and targets of a DoS attack may vary, it generally consists of the efforts of one or more people to temporarily or indefinitely interrupt or suspend services of a host connected to the Internet.” [Wikipedia 2012]
Background
For the past years, website defacement is harmless and the purpose of attackers is only for fun. The action in defacement is page modification. But in recent years, website defacement has been used for business competition and even for political conflicts among countries. Especially in Asia, many attackers in different countries deface the websites of companies and government of other countries because of the international conflicts on sovereignty and territory.
Means of cyber attacks are not confined to website defacement, but more DoS and DDoS attacks were used. The BBC News reported in April of this year that an anonymous hacking group claimed to have defaced almost 500 websites in China. The websites affected included government sites, trade groups and many other sites. And attackers put messages on the defaced websites in order to protest against the Chinese government [BBC News 2012]. Besides China, many websites in other countries such as Japan, Philippine and Vietnam are also attacked by hackers because of different purposes. For example, the Atlanta IT Service reported in 2011 that a server in China was used to attack on the Japanese Lower House. Many emails and documents had been penetrated and some passwords and user IDs may have been stolen [Atlanta IT Service 2011].
Methods
The methods used in defacement are very similar which cover vulnerable servers scanning and uploading backdoors to report infected servers [David and Tim 2010]. These two analysts also indicated that attackers often utilize “Google Dorks” which is a specially crafted search query to identify vulnerable servers. The tools used by defacers to check vulnerable servers include LFI intruder, VopCrew IJO Scanner, SCT SQL scanner and Osirys SQL RFI LFI scanner etc.
Defacement Record
With the website defacement has been harmful to countries all over the world, some archives, documents and news started to record these defacements happening every day. One of the websites recording defacements around the world is the “Zone-h”. It archives defacements each day and classifies defacements into homepage defacement, mass defacement, re-defacement and special defacement, which is for important websites. And the analysts in Zone-h will verify these records in on-hold list to delete the fake notification. We have analyzed the record for 12th, October, 2012. In this daily record one defacement to Japanese website, one defacement to Vietnamese website and nine defacements to Chinese websites were recorded in the archive of this day. For the defacements to Japanese website and Vietnamese website, the two defacements were classified in homepage defacement and no special defacement to important website was notified. As some of the defacements to China covered all the three defacements, eight out of the nine are homepage defacements, two are mass defacements, three are re-defacements and four are special defacements, and all the special defacements are aiming at websites of Chinese government. Furthermore, in the 11 defacements, all the Chinese websites are built on servers with Win 2003, and the Japanese website and Vietnamese website are built with Linux.
Besides the general record, there is an archive for recording the special defacement provided by Zone-h. We have analyzed the special records from 1st October to 12th October. We found that 4 defacements to Vietnamese government websites and 105 defacements to Chinese government websites happened in this period. In the defacements to Vietnam, 2 are homepage defacements and two are mass defacement with multiple IP addresses. And in the defacements to China, 48 are homepage defacements, 35 are mass defacements and 25 are re-defacement by a single IP address. According to the origin countries of these defacements, the hack defaced the most Chinese websites is Barbaros-DZ from Algeria.
As we didn’t find defacement record about Philippine in Zone-h, we tried to find some articles mentioning information about website defacement to Philippine. [Adam 2012] described that because of conflict about Huangyan Island, Chinese hackers attacked the websites of Department of Budget and Management and the University of Philippines, and also posted Chinese flag on Philippines News Agency site.
Cyber-attacks events
“In September 2012 at least 19 Japanese governmental and other websites has been attacked. Out of these 19 sites, 11 are a victim of DDoS attacks, and include some really important sites like banking, power utility, and other private-sector companies–on the public side include government agencies such as the Defense Ministry and the Internal Affairs and Communications Ministry. The remaining 8 websites were vandalized, including those of the Supreme Court and the Tokyo Institute of Technology, leading them to display pictures of the Chinese national flag. Continuing the list, Tokyo Institute of Technology’s site was defaced, and further endured an attack that saw names and telephone numbers of over 1,000 members of staff leaked.” Japanese National Police Agency originated these attacks in China.
“Japan’s top weapons maker Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) has confirmed it was the victim of a cyber attack reportedly targeting data on missiles, submarines and nuclear power plants. Viruses were found on more than 80 of its servers and computers. They have been described as spear phishing attacks – when hackers send highly customized and specifically targeted messages aimed at tricking people into visiting a fake webpage and giving away login details. A plant in Nagoya, where the company designs and builds guidance and propulsion systems for rockets and missiles, was also reportedly compromised. A second defense contractor, IHI, which supplies engine parts for military aircraft, said it had also been targeted. IHI said it had been receiving emails containing viruses for months, but its security systems had prevented infection. There are also reports that Japanese government websites, including the cabinet office and a video distribution service, have been hit by distributed denial-of-service attacks. Neither the Japanese government nor MHI have said who may be responsible. A report in one Japanese newspaper said Chinese language script was detected in the attack against MHI. But China rebuffed suggestions it could be behind the attacks.”
On Apr 20, 2012 Chinese hackers attacked the University of Philippines” website. They defaced the UP website (up.edu.ph) with a map, labeled with Chinese characters, showing the Huangyan Island.
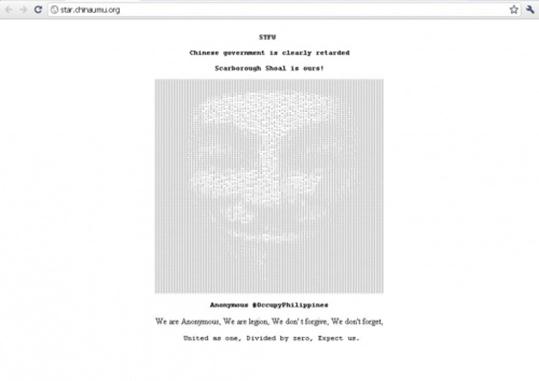
On Apr 21, 2012 Filipino hacktivists quickly stroke back at Chinese websites (star.chinaumu.org, v.cyol.com, ploft.cn, sanxinsudi.com, gh.rc.gov.cn, ryjzw.com, lanseyinxiang.com)
On Apr 23, 2012 some Philippines’ official websites (pcdspo.gov.ph, malacanang.gov.ph) were attacked with a DDOS attack by hackers whose IP addresses are assigned to Chinese networks.
On Apr 24, 2012 Filipino hacktivists took down more Chinese websites in response of attack made by Chinese hackers.
On Apr 25, 2012 an online forum of Chinese hacker posted usernames and passwords of Bulacan provincial government website administrators. A member of the ‘Honker Union’ published on Facebook the alleged usernames and passwords of administrators of websites belonging to Philippines’ government (rmn.ph, kal.upd.edu.ph, pmap.org.ph).
On Apr 25, 2012 the website of Filipino Department of Budget and Management was defaced, and quickly taken down for a “security audit”. Meanwhile, at least three other government websites were taken down for DDoS attacks.
From Apr 26 to 30, 2012 Filipino hacktivists took down 5 Chinese government sites.
On May 4, 2012 the website of National newspaper Philippine Star was defaced with a message “Warning. Philippines, China inviolable state sovereignty”
“The Vietnamese media has also been reporting on those cyber attacks. According to Thanh Nien News, 200 Vietnamese websites were attacked in June, and 10 percent of those websites were managed by government agencies. For example, 20 websites under the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development were hacked. A source from the ministry’s network security supporter said that they have identified that the Internet protocols (IP) of computers attacking the portal were from China. According to some Chinese bloggers, they believe the attacks started by Honker Union, a mysterious hacker organization in China formed by young people with sophisticated computer skills. However, the Vietnamese also began their retaliation. Several Chinese websites were also under attacks by Vietnamese hackers.”
Severe Situation in the Asian-Pacific Region
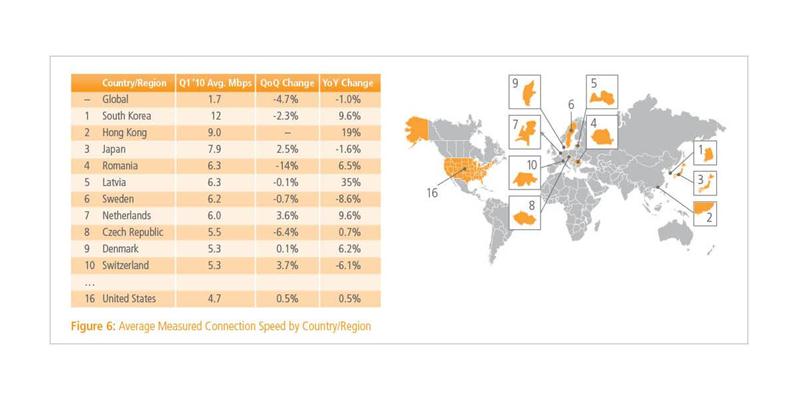
In 2012 first quarter, the broadband connection speed increases 25%, especially in Asian-Pacific region. The cyber attacks are more severe with the spread and higher speed of the network. The top 10 countries which have most frequent cyber attacks are reponsible for 77% of all the cyber attacks in the world. Almost 42% of worldwide cyber attacks are from the Asian-Pacific region according to the report from Akamai Company. China and Japan both have a high rate in this case. The cyber attacks between Asian countries increase together with the complicated political situation and recent Island dispute.
The island dispute between Japan and China is moved to cyber realm. Japan Police Department (JEM) and the Japanese government have been hit by public organizations and internet sites in the middle of September. The Japanese Safety is often attacked and its content has been changed and becomes online site. JEM thinks those hacker attacks seem to be from China, which cause double Japanese attacks.
The Japanese Defense Officials revealed the details for cyber attacks between Japan and China and indicated that the recent series of cyber attacks originated in China were viewed as a possible prelude to millitary action in Island dispute event.
Japan’s National Police Agency showed that dozens of Japanese websites were hit by cyber attacks, which increases the tensions between Tokyo and Beijing.
The defacement attack often takes place related to politics matters. In order to responde the attacks in University of the Philippines (UP). Chinese University Media Union (UMU) is attacked by a group of Philippine hackers. The main page of the website is defaced by a picture and screming music played in the background: “Scarborough Shoal is ours”.
Reference
http://www.atlantaitservice.com/cms/technews/japan-under-heavy-cyber-attack
http://www.securelist.com/en/analysis/204792127/Mass_Defacements_the_tools_and_tricks
http://www.theregister.co.uk/2012/09/21/japan_china_attack_sites_senkaku/
http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-asia-pacific-14982906
http://hackmageddon.com/2012/05/01/philippines-and-china-on-the-edge-of-a-new-cyber-conflict/
http://talk.onevietnam.org/cyber-war-started-between-china-and-vietnam-over-spratly-islands/
http://www.akamai.com/html/about/press/releases/2012/press_080912.html
http://www.habermonitor.com/en/haber/detay/cyber-attack-from-china-to-japan/237323/
http://glblgeopolitics.wordpress.com/tag/chinese-origin-cyber-attacks/
http://www.broowaha.com/articles/13319/filipino-hackers-retaliates-defaces-chinese-websites